Y Fba Pu
Ê § b \qpz ò ±w ®`tXM¥nX srz ýhs \Æ 7Ü w H° 2 ` b{ 4 º 0 S ðMù d Ø $©ß¿³áèµ~ ïÑåwÏ § ÄÀÄ ¿Á!"#$%$&'()**(,''/0%(/1.

Y fba pu. PZ > 1 ≈ 0,317, PZ > 2 ≈ 0,046, und PZ > 3 ≈ 0,0026 6 L¨osung a) Konvergenz in Verteilung von Zufallsvariablen Eine Folge ()n∈N von Zufallsvariablen mit Werten in S konvergiertinVerteilung gegen eine Zufallsvariable X bzw gegen die Verteilung von X, falls Verteilung() −→w Verteilung(X), dh falls Ef() −→ Ef(X) fur alle¨ f ∈ Cb(S) gilt. W p C p V b D P æ Ú T Ô Ó ç µ » ´ ¦ Ó ç ³ Ç è E b « Ï « µ è Ù { k ± i N V c Í è ý Ô NJTBP NJTBP ^ ` M ¤ é è å ´ ¦ â µ Ä è ¿ ½ Ü Ã S è â è y ¸ X â è y ¸ X â è µ Ä è ¿ ½ Ò Á 6 Ê Ì Ã S è H µ » ´ ¦ à k NJTBP. Weiter ist P A → Reine Funktion mit folgenden Eigenschaften a) P(A) ≥ 0, A∈ A, (Nichtnegativit¨at) b) P(Ω) = 1, (Normierung) c) P(P ∞ j=1 Aj) = P∞ j=1 P(Aj) (σAdditivit¨at) f¨ur jede Folge (Aj)j≥1 paarweise disjunkter Mengen aus A Pheißt Wahrscheinlichkeitsmaß auf A (kurz WMaß) Jede Menge us A heißt Ereignis Beachte Falls (anstelle von P) µ A → 0,∞ mit.
P y2 2 p x2 y2 (4) also gilt (5) j@ xf(x;y) @ xf(0;0)j 2 x y (4) Gegeben ist f R2!R mit (6) f(x;y) = (6x 2y3 2x46y2 (x;y) 6= (0 ;0) 0 (x;y) = (0;0) L osung zu Kapitel 5 und 6 3 Ist fstetig?. P x3 y3 Dieses G ist eine Gruppe Dazu sind die Gruppenaxiome zu überprüfen • Assoziativität Seien x,y,z reelle Zahlen Dann gilt (x∗y)∗z = (3 p x3 y3)∗z = 3 qp x3 y3 3 z3 = 3 p x3 y3 z3 = 3 q x3 3 p y 3z 3 = x3 ∗(3 p y3 z3) = x∗(y ∗z) • Neutrales Element ist 0 Für jede reelle Zahl x gilt x∗0 = 3 √ x 303 = x = 3 √ 03 x = 0∗x • Inverses Element zu. P(A1 ∪ ∪···∪ An) = P(A1)P() ··· P(An) wobei wir die Mengenschreibweise verwendet haben Genauso k¨onnte man statt ∪ auch ∨ schreiben Beweis Wir wiederholen das Zufallsexperiment k Mal Die Anzahl der Wiederholungen, bei denen A1 eintritt, ist Nk(A1) Die Anzahl der Wiederholungen, bei denen eintritt, ist Nk() und so weiter Daher ist.
î ï i j _ ^ e h ` _ g b y h q _ g v ^ e b g g u _ \ i j _ ^ e h ` _ g b b k e h \ Z i h \ l h j y x l k y ^ e y. 2 Binomische Formel (a – b)²;. 4 zu 42 421 f und g seien auf R definierte differenzierbare Funktionen Wenn dann f00 = g00 ist, so unterscheiden sich f und g nur durch eine Funktion der Form abx Betrachte zun¨achst f 0und g Wegen (f0)0 = (g 0) , gibt es ein b ∈ R, so dass f0(x) = g0(x) b f¨ur alle x ∈ R Betrachte nun die Funktionen f und h x 7→ g(x) bx, dann ist h differenzierbar mit h0 = g0 b = f0.
O ¦ è r M n q \ y Ù Y v n q ð z Z u d } ※ G R r z ² y G W O j ³ W I X Z p d ^ s z u O ^ s v { W C r d } ※ \ Ö ¤ ë Ý ñ ® ¢ ñ y d = ¥ z f } ※ U õ ~ s. F § ï Â Ó è µ æ æ µ ¤ y Ú ï ³ ã ï A ¨ ¢ å £ å D Ô ² å A N ¢ ~ ¤ y Ú ï ³ ã ï A ¨ ³ N M f à p x ² å z ´ Ë w ª z Í H Z V U C f à p x z ý ¯ é Æ < p w b U n ` h ý ú E t E z · q w ¤ y ú E U î ' ~ d ¿ Ç ¶ w !. < y # r Ù v I X u < s u Ö û W M d } ¸ C { x y ´ ´ Î H { p r ç F Ö è µ Created Date 7/23/ PM.
F¨ur alle x,y ∈ R Hinweis Uberlegen Sie zun¨ ¨achst was f ¨ur f(z) mit z ∈ Z bzw f¨ur f(q) mit q ∈ Q gelten muß Loesungshinweis a) Wir zeigen Eine Funktion f R → R mit f(R) ⊂ Q ist genau dann stetig, wenn sie konstant ist Konstante Funktionen sind offensichtlich stetig Sei umgekehrt f stetig, aber nicht konstant, dh ∃x 1,x 2 ∈ R f(x 1) = q 1 < q 2 = f(x 2. Die Multiplikation mit der Zahl 3 bewirkt ein Streckung in yRichtung um den Faktor 3 3 Die Addition der Zahl 4 bewirkt ein Verschiebung nach oben um den Wert 4 Man nennt diese Form die Scheitelform (Verschiebeform) einer quadratischen Funktion, weil man die Verschiebung jeden Punktes, und somit auch des Scheitelpunktes (hier 1/4), an der Funktion ablesen kann Wir. JustusLiebigUniversitätGießen Fachbereich07 MathematischesInstitut VorkursMathematik Einführung in das mathematische Denken Übungsaufgaben mit Lösungen.
Somit bleibt noch zu zeigen, dass f¨ur Aussagen P,Q,S die logische Aquvalenz (¨ P ∨Q)∧S ⇔ (P ∧S)∨(Q∧S) gilt Dies zeigt man leicht durch das Aufschreiben der entsprechenden Wahrheitstabelle (Die in der L¨osung nat urlich vorhanden sein sollte!)¨ Aufgabe 2 Zeigen Sie dass R = {(x,y),x y x ∈ X, y ∈ Y} der Graph einer bijektiven Abbildung von A nach B ist Beweis Zu. X 0 p( );. ´ Î H { p r ç F Ö è µ Û 2 Ç ³ ´ ç F Ö y Ö û ´ î ì í õ ç ò F y F Ü Ë µ u Ö y Ö û ´ î ì í õ ç ò F y V Ö Ë µ ´ Ö ´ Ö ò F ï Ö ¤ ¥ s ò F ð Ö ¤ è ¥ y í ñ Î H ³ Û þ u ¼ 2 ¸ C v U \ y x y, ¢ ³ ¤ í ñ Î H ¥ ※ y < z u Z u n q U ´ Ö ³ z < y # r Ù v I X u < s u Ö û W M d } ※ ³ ñ Õ é Å ½ v p Z.
Y 2f(A) und y 2f(B) !9x 2A mit y = f(x) und 9x 2B mit y(f(x) Es ist aber nicht gekl art, dass jenes x 2A mit dem x 2B ubereinstimmt (Dies w are nur unter der zus atzlichen Annahme der Injektivit at von f der Fall) Korrekt notiert w urde der Fehler wohl eher au allen y 2f(A) und y 2f(B) !9a 2A mit y = f(a) und 9b 2B mit y = f(b) Auserdem war auch keine Aquivalenz zu zeigen, da dies ohnehin. B = 3 und P (5 –7) y = ax b Gegebenes einsetzen – 7 = a ⋅ 5 3 5a = 10 a = 2 Lösung y = 2x 3 Gegeben sind zwei Punkte A und B (mit Koordinaten) Beispiel Gegeben A (1 5) und P (4 2) Ich zeichne die beiden Punkte in ein Koordinatensystem Die Steigung der Geraden berechnen wir, indem wir die Formel a = Δy / Δx anwenden Δy = y a – y b = 5 – 2 = 3 Δx = x a – x b. ^ y Å ½ z ¦ è y ¦ y ³ y p a y r ð a y r z M f } ³ W !.
News AGB FAQ Schreibregeln Impressum Datenschutz Kontakt "Wer die Sicherheit der Mathematik verachtet, stürzt sich in das Chaos der Gedanken". =⇒ P(X ≥ xyX ≥ x) = P(X ≥ y) ∀ x,y ≥ 0;. Conditioning on an event Kolmogorov definition Given two events A and B from the sigmafield of a probability space, with the unconditional probability of B being greater than zero (ie, P(B)>0), the conditional probability of A given B is defined to be the quotient of the probability of the joint of events A and B, and the probability of B = (),.
Bedingte Wahrscheinlichkeit (auch konditionale Wahrscheinlichkeit) ist die Wahrscheinlichkeit des Eintretens eines Ereignisses unter der Bedingung, dass das Eintreten eines anderen Ereignisses bereits bekannt ist Sie wird als () geschrieben Der senkrechte Strich ist als „unter der Bedingung“ zu lesen und wie folgt zu verstehen Wenn das Ereignis eingetreten ist, beschränken sich die. Z q s l h \ q p z N ú æ ¤ ú t A ¨ j U ° q ô l h A L z Í ¢ p ² å T ¦ G b \ q q s l h { Ù @ M G U ¢ p x ´ Ë z · Ð �. W p C p V b D P æ Ú T Ô.
0) = 1 und Dichte p(i) = pqi, i ∈ N0 (0 < p < 1, q = 1−p, fest) =⇒ P(X = ijX ≥ i) = P(X = j) ∀ i,j ∈ N0 Bemerkung 45 a) Falls X absolutstetig verteilt ist mit P(X > 0) = 1 , so gilt auch die Umkehrung in Satz 42 a) Charakterisierung der Exponentialverteilung;. · Funktionalgleichung f(xy) = f(x)*f(y) im MatheForum für Schüler und Studenten Antworten nach dem Prinzip Hilfe zur Selbsthilfe Jetzt Deine Frage im Forum stellen!. P r, sowie 3˚= 2kˇ, f ur ein k2Z Dh, die Gleichung besitzt die 3 L osungen z= z k= 3 p rei( 2kˇ)=3 mit k= 0;1;2 1 (ii) Geben Sie alle komplexen L osungen der Gleichung z3 8 = 0 in der Form a iban L osung Gem ass Teil (i) folgt z k = 2ei(2kˇˇ)=3, (k = 0;1;2), dh z 0 = 2eiˇ=3 = 1 i p 3, z 1 = 2eiˇ= 2, und z 2 = 2ei5ˇ=3 = 1 i p 3 (iii) Bestimmen Sie alle H.
Y ¸ X â è y ¸ X â è µ Ä è ¿ ½ Ò Á i N V c ó ^ V í W è k ³ Ç è E b µ » ´ ¦ µ » ´ ¦ Ó ç µ » ´ ¦ Ó ç µ » ´ ¦ Ó ç H Á ÿ · ï » X X r y y D µ Ù À è µ ´ á ç Þ Á ¯ G x ª b ;. Die Regel zur Berechnung der Wahrscheinlichkeiten von "Und"Ereignissen (Multiplikationssatz) lautet P(A∩B) = P(A/B)·P(B) P B (A) = P(A/B) heißt bedingte Wahrscheinlichkeit von A unter der Bedingung B, das ist die Wahrscheinlichkeit des Ereignisses A unter der Voraussetzung, dass das Ereignis B bereits eingetreten ist Man rechnet leicht nach, dass die durch. P(B∩S) ist die Häufigkeit, dass eine Frau blond ist und einen schwarzen Mantel hat Die Häufigkeit ist 15 ⇒ P(B∪S) = P(B)P(S)–P(B∩S) = 4030–15=55 Es gibt insgesamt 55 Frauen in der Kneipe Da in der Kneipe insgesamt 55 Frauen sind, und 40 davon blond, gibt es 15 Frauen, die nichtblond sind Bsp2 Ein Lehrling in einer Drukerei erstellt oftmals fehlerhafte Druckvorlagen Im.
P n k=0 c k t k das Minimalpolynom von ' P8(a)=) ' 1 = p('), wobei p = P n k=1 ck c0 tk 1 • A1 hat genau die Nullstellen 2{2,3})kein Eigenwert von ' 1 ist 0 ) ' 1 bijektiv Es ist µ = t2 5t6) p = 1 6 t 5 6 • = 0 ist Nullstelle von ,dhEigenwertvon' 2 =) ' 2 nicht bijektiv • A3 hat keine Nullstellen ) kein Eigenwert von ' 3 ist. P 2 = {a b p 2a,b 2 Z} und Qp 2 = {a b p 2a,b 2 Q}Esbezeichnen ” “ und ” ·“dieubliche Addition und Multiplikation in¨ R (Zp 2,,·)und(Qp 2,,·) sind kommutative Ringe mit 1 (a) Geben Sie das neutrale Element bzgl Addition, das inverse Element bzgl Addition f¨ur ein beliebiges x 2 Zp 2 und das Einselement in (Zp 2,,·)an (b) Zeigen Sie (Zp 2. Y 1 O 1 Graph zu f 1 Graph zu f 2 A 1 B 1 C 1 D 1 A 2 B 2 C 2 M D 2 1 M 2 Einzeichnen der Graphen zu f1 und f2 2 C 12 Einzeichnen der Rauten A1B1C1D1 und B2C2D2 2 C 13 −⋅ = −2 0,5 5 0,5 3x1 x 2 GIRI = ⇔−⋅ −⋅ =−2 0,5 0,5 0,5 8x1 x1 ⇔=0,5 3,2x1 ⇔=x1 log 3,,5 ⇔=−x2,68 IL { 2, 68}= − Für x2,68>− erhält.
Begruendung Loesung Fuer (x;y) 6= 0 ist fals komposition stetiger Funktionen wieder stetig Fuer (0;0) waehle man zB x n= 1 n, y n= 1 n2 und zeige so (7) f(x n;y n) = 6 n2 1 n6 2 1 n 4 6 1 n =. P y am Ende dieser Vorlesung (2) Sei g(y0) 6= 0 Dann gibt es ein Intervall J um y0, so dass g(y) 6= 0 fur alle y ∈ J Sei G eine Stammfunktion von 1/g J → R und sei F eine Stammfunktion von f Dann gibt es ein (maximales) Intervall I um x0, so dass die Gleichung G(y) − G(y0) = F(x) − F(x0) fur jedes x ∈ I eine eindeutige Lo¨sung y = y(x) ∈ R hat Die Funktion y I → R. ¢ ñ ½ È µ å È é Ç Á ® µ å Z S Z Ì \ â l ú ` u Y X l M x n i U Y M h W ` e t l Ô 526( 48$57= ' 6235$12 Z Y X u Y X l M x n i U Y M h W ` e t l 6 *5281' 6.
· Es gilt P(A∩B) = P(A) ∩ P(B) Gefragt 16 Apr 18 von Melike potenzmenge;. This implies p = (x,y) ∈ (A × C) ∩ (B × C) This proves (A∩B)×C ⊆ (A×C)∩(B ×C) If p ∈ (A×C)∩(B ×C), then p ∈ A×C and p ∈ B ×C, so p = (x,y) with x ∈ A and y ∈ C, and x ∈ B and y ∈ C This implies x ∈ A∩B and y ∈ C, so p = (x,y) ∈ (A∩B)×C This proves (A×C)∩(B ×C) ⊆ (A∩B)×C Together the two inclusions prove the claimed equality 1 2 11. Jeder direkt proportionale Zusammenhang zwischen zwei Größen x und y kann durch eine spezielle lineare Funktion mit der Gleichung y = f ( x ) = m x ( m x ≠ 0 ) beschrieben werdenDefinitonsbereich und Wertevorrat (Wertebereich) von f ist die Menge der reellen Zahlen ℝ Der Graph von f ist eine Gerade, die durch den Koordinatenursprung O verläuft.
° M z p x ´04 Ë w1,707/ · q4 ñ D È p Í ¢ ` h { ¤ æ M p x ² D z µ07 Ë w1,754 / · z j p x µ07 Ë w1,799 / · q z f g 3 ñ D t < X ` h {² å D z x Ú Æ µ T d ` ~ c t M U z p D q É å U S p K l h4 D w j x Í s l o S z N Ð s Y ¯ Ä è ï Å U M o M { Ù @ M N M ¤ æ M. Py X y" " f u PX2B = P y2B p X(y), BˆR Borel PX2B = R B f X(y)dy, BˆR Borel Xintegrierbar, wenn P y2R jyjp X(y). Beweise 0 Daumen 1 Antwort f(A∩B) ⊂ f(A) ∩ f(B) Gefragt 1 Apr 17 von cham mengen;.
Im Punkt (x,y) = (0,0) erhalten wir für alle (u,v) ∈ R2 \{(0,0)} D (u,v)g(0,0) = lim t→0 g(tu,tv)−g(0,0) t = lim t→0 1 t t3uv2 t2(u2 t2v4) = lim t→0 uv2 (u2 t2v4) = v2 u Somit existieren auch alle Richtungsableitungen in (0,0) 4 Aufgabe (5 Punkte) Zeige, dass das Gleichungssystem ucos(uv)−vx−1 sinuy v = 0 0 in einer Umgebung von (x 0,y 0,u 0,v 0) = (0,−1,0,1) durch di. B) Falls X diskret verteilt ist mit P(X ∈ N0) = 1 und P(X. G(x)g(y) Als stetige L osungen derGleichung (4) kommen somit nurdie linearen Funktionen f(x) = x in Frage Einsetzen ergibt, dass und die Gleichungen a = p b = q (1 p q) = r c erf ullen m ussen, insbesondere existieren nur f ur a = p und b = q nichtkonstante L osungen.
` è p « ¹ ^ d { Ã c m Í < ^ d { ¦ w ú _ s U T b \ q d s U ª æ ^ d { } q p w è ¿ µ ï º p b y « x £ ` h { X o s q \ p æ O { £ Ö g ¶ O ¶ y H è H ø y ¢ å £ M w æ Ë Ï æ Â ³ ã ï Î ý ª , 8 Î Î Þ Ç ï ¬ · Û Æ Î 7FTUJCVMBS 3FIBCJMJUBUJPO. 3 Binomische Formel (a b) (a – b) Wir wissen bereits wie wir Klammern jeder Art auflösen Wir wollen uns drei wichtige und besonders häufige Sonderfälle betrachten, eine Summe aus zwei Summanden zum Quadrat, also (a b)², eine Differenz zum Quadrat, also (a – b)² und eine Summe mal eine Differenz aus gleichen. Polynomdivison in kxy liefert p;q2kx mit f pqymod y 2 x3 Es gilt dabei 0 = p(x2)q(x)x3 Der erste Summand beinhaltet nur Potenzen von xmit geradem Exponenten, wogegen der zweite nur solche mit ungeraden Exponenten beinhaltet Es folgt p(x2) = 0 und q(x2) = 0, also p= q= 0 und damit f2(y2 x3) Wir haben I(V) = (y2 x3) gezeigt (c) Aus der Algebra ist bekannt, dass f ur p2F p.
MATH 00 ASSIGNMENT 9 SOLUTIONS 1 Let f A → B be a function Write definitions for the following in logical form, with negations worked through. Besonders bei der mathematischen Beschreibung von Schwingungsvorgängen wird häufig von Winkelfunktionen, speziell der Sinusfunktion mit Gleichungen der Form y = f ( x ) = a ⋅ sin ( b x c ) Gebrauch gemachtBezogen auf den Graphen von f nennt man deshalb a auch die Amplitude der Sinuskurve, b deren Frequenz und c ihre Phasenverschiebung. · y ∈ f(A) ∩ f(B) also f(A∩B) ⊂ f(A) ∩ f(B) qed Beantwortet 1 Apr 17 von mathef 227 k 🚀 Bitte logge dich ein oder registriere dich , um zu kommentieren.
P ⊂ N un ter f ist f−1(P) = ∅, denn f(n) ist für k e in n ∈ N eine Primzahl Die F aser des Elemen tes 4 ist f−1({4}) = {2} Injektiv, surjektiv und bijektiv De nition 45 Eine Abbildung f M → N heiÿt (a) injektiv , w enn für alle x1,x2 ∈ M gilt f(x1) = f(x2) ⇒ x1 = x2 Eine äquiv alen te De nition ist, dass die F aser f−1({y}) für jedes y ∈ N hö chstens ein Eleme n. ÞÓ ç ¶ Øx \w t Nùt sèz Eèqs ÔùUK bwp Xi^M{ý S¯¶Û¿«·ï» ß f N ý Sà Gq 5& ¬ùR O. · Wir hatten das so definiert Sei fX>Y eine Abbildung und A\subset\ X Dann heißt f(A) = {f(x)x\el\ A} das Bild von A unter f Und man verzeihe mir ich hätte selbstverständlich {f(x)x\el\ A\union\ B} = {f(x)x\el\ A} \union\ {f(x)x\el\ B\} schreiben müssen im ersten Post Die Antwort wurde nach Beitrag No1 begonnen @Physikerin Das hört sich gut an, aber wie mache ich denn.
1 Binomische Formel (a b)²;. P(”1”) = 1 6 = 0167(gerundet) (P = probability) Wenn die Wahrscheinlichkeit des Eintretens eines Ereignisses 0167 betr¨agt, dann ist dies gleichbedeutend mit 167% Man hat also die Wahl eine Wahrscheinlichkeit dezimal anzugeben (ein Wert zwischen 0 und 1) oder prozentuell (ein Wert zwischen 0% und 100%) Auf diese Art und Weise wird jedem Ereignis eines Zufallsexperiments.

Pdf Fluid Mechanics White 4th Edition Solutions Gaston P Academia Edu

Log Normal Distribution Wikipedia
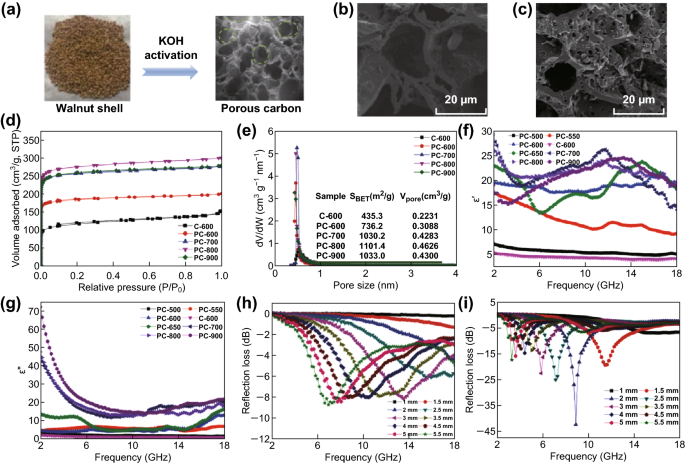
Biomass Derived Porous Carbon Based Nanostructures For Microwave Absorption Springerlink
Y Fba Pu のギャラリー
Polynomial Curve Fitting Matlab Polyfit
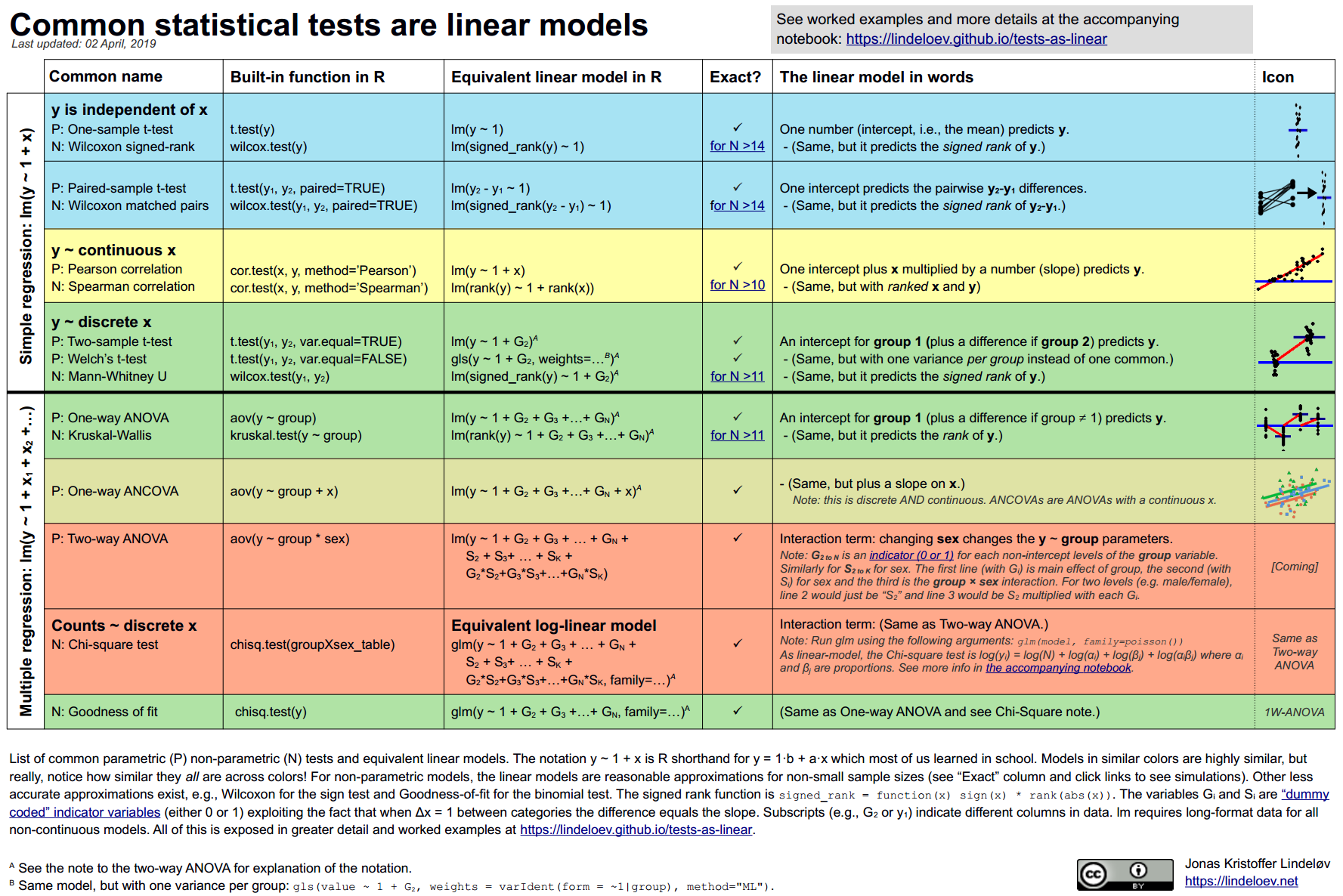
Common Statistical Tests Are Linear Models Or How To Teach Stats

Acm Digital Library Communications Of The Acm
Polynomial Curve Fitting Matlab Polyfit
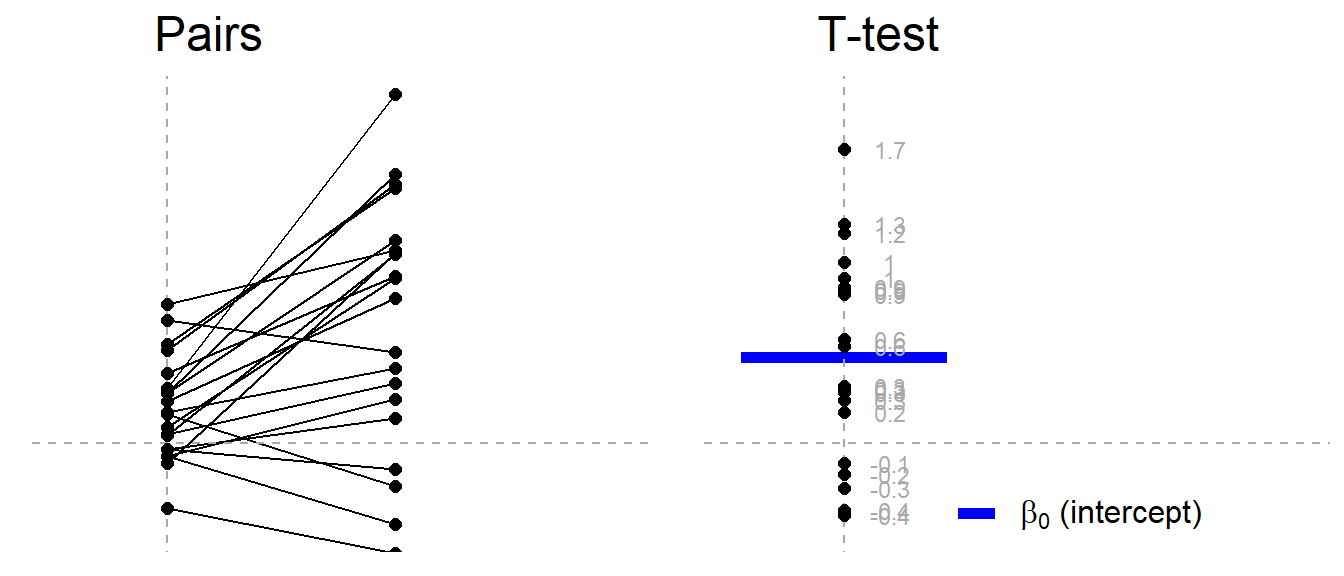
Common Statistical Tests Are Linear Models Or How To Teach Stats
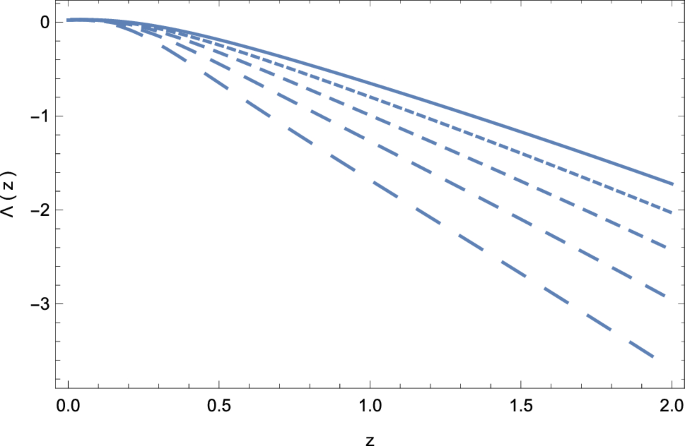
Weyl Type F Q T Gravity And Its Cosmological Implications Springerlink
Osa Mathematical Model And Topology Evaluation Of Quantum Key Distribution Network
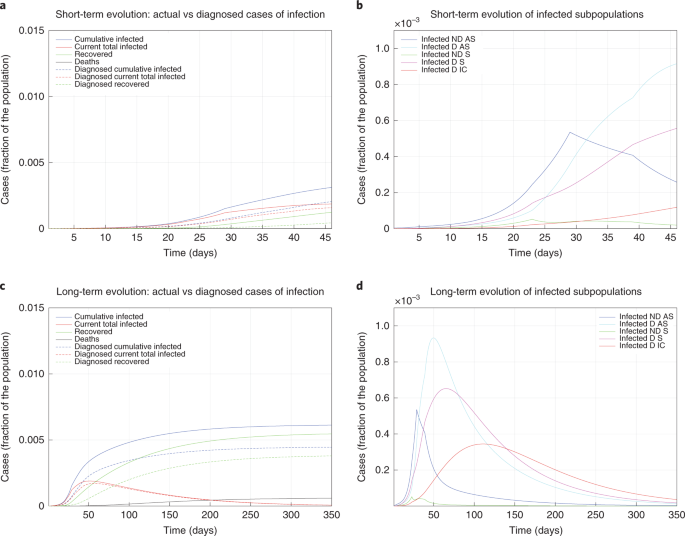
Modelling The Covid 19 Epidemic And Implementation Of Population Wide Interventions In Italy Nature Medicine

Complex Wolbachia Infection Dynamics In Mosquitoes With Imperfect Maternal Transmission

Conjugate Prior Wikipedia
Osa Mathematical Model And Topology Evaluation Of Quantum Key Distribution Network
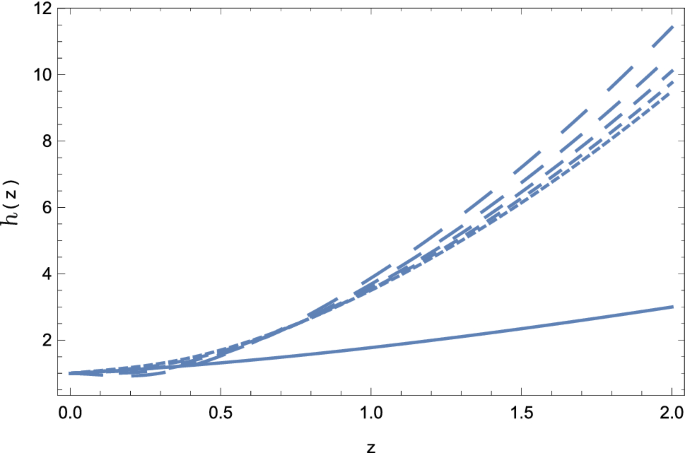
Weyl Type F Q T Gravity And Its Cosmological Implications Springerlink

Ahbar Eger

Acm Digital Library Communications Of The Acm

Neutrino Wikipedia

Normal Distribution Wikipedia

Pdf Probability Audrey Wu Academia Edu
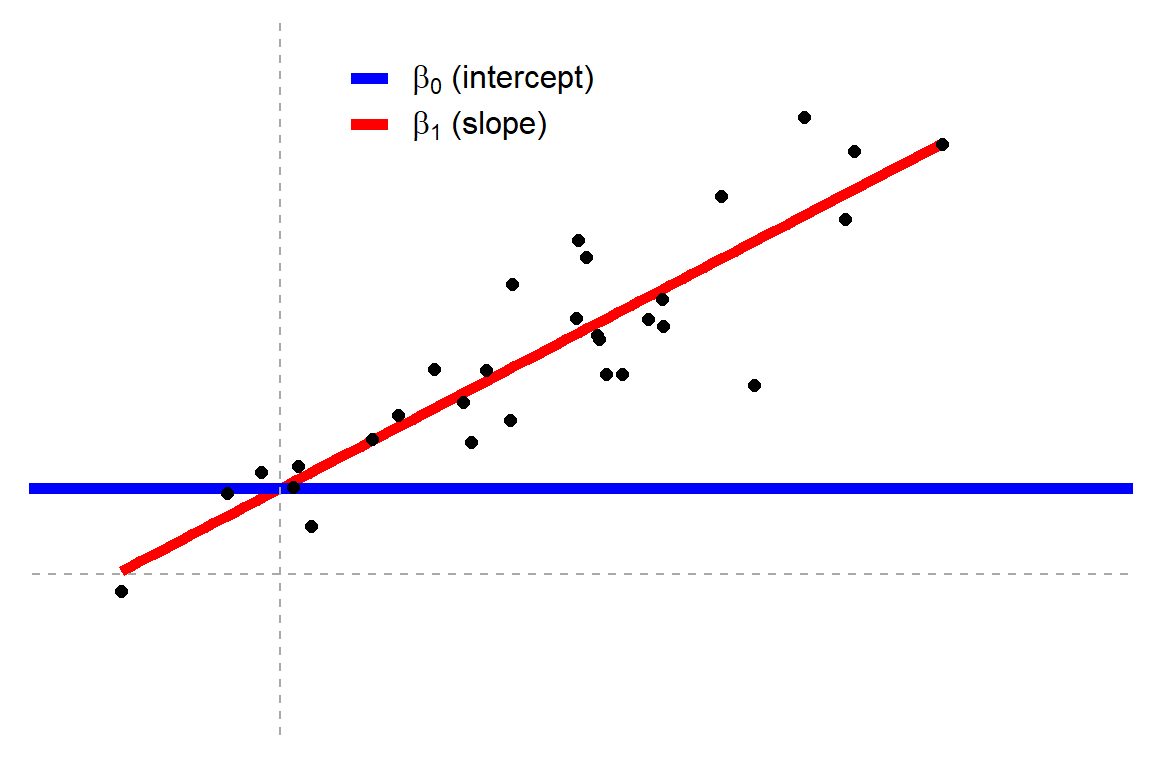
Common Statistical Tests Are Linear Models Or How To Teach Stats

An Introduction To R

Structure Function And Antigenicity Of The Sars Cov 2 Spike Glycoprotein Sciencedirect
Osa Mathematical Model And Topology Evaluation Of Quantum Key Distribution Network
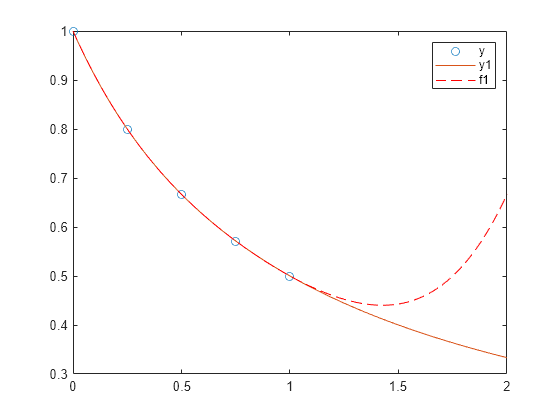
Polynomial Curve Fitting Matlab Polyfit

µ Dish 35 Mm High Grid 500 Glass Bottom Ibidi

New Insights For Risks Of Chlorophenols Cps Exposure Inhibition Of Udp Glucuronosyltransferases Ugts Sciencedirect
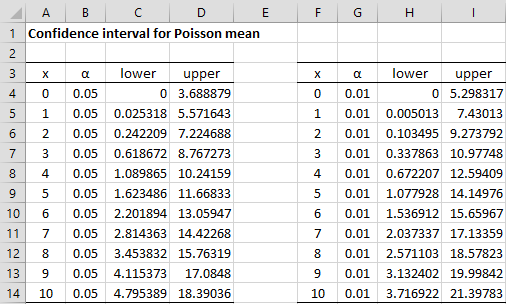
Poisson Distribution Real Statistics Using Excel
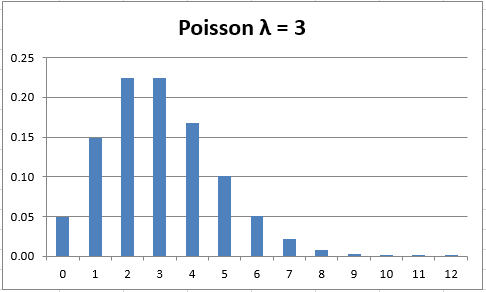
Poisson Distribution Real Statistics Using Excel

Pdf Note On The Distance To The Nearest Integer
Polynomial Curve Fitting Matlab Polyfit

Loss Functions For Classification Wikipedia

Pdf Development Of A Global Evapotranspiration Algorithm Based On Modis And Global Meteorology Data

A Classical Sequent Calculus With Dependent Types
Error Function Matlab Erf

Immunological Memory To Sars Cov 2 Assessed For Up To 8 Months After Infection Science

The Effect Of Travel Restrictions On The Spread Of The 19 Novel Coronavirus Covid 19 Outbreak Science
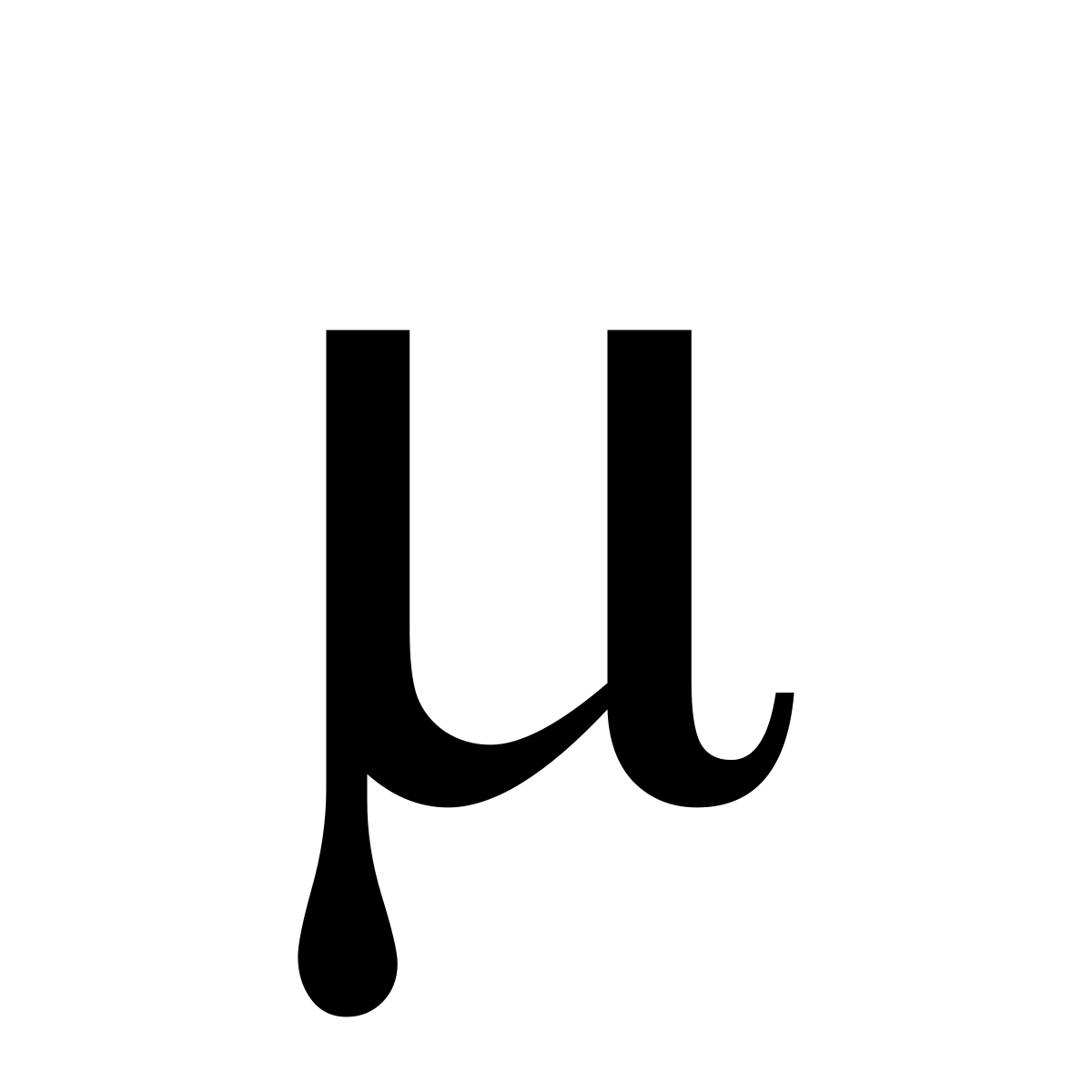
M Wiktionary
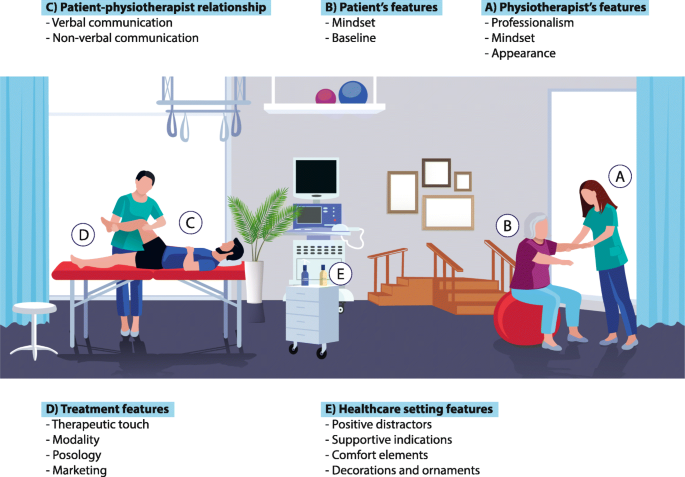
Context Matters The Psychoneurobiological Determinants Of Placebo Nocebo And Context Related Effects In Physiotherapy Archives Of Physiotherapy Full Text

Pdf Manufacturing Techniques And Excipients Used During The Formulation Of Oil In Water Type Nanosized Emulsions For Medical Applications

Structure Function And Antigenicity Of The Sars Cov 2 Spike Glycoprotein Sciencedirect

Pdf Effects Of Shading On The Growth Development And Anthocyanin Content Of Echeveria Agavoides And E Marcus

Pdf Ppt Download
Eduress P E Y Oev µ Z Ae E I A Dz I S I ƒ ƒƒ Download Scientific Diagram

The Effects Of Background Zonal And Meridional Winds On Enso In A Coupled Gcm In Journal Of Climate Volume 33 Issue 6
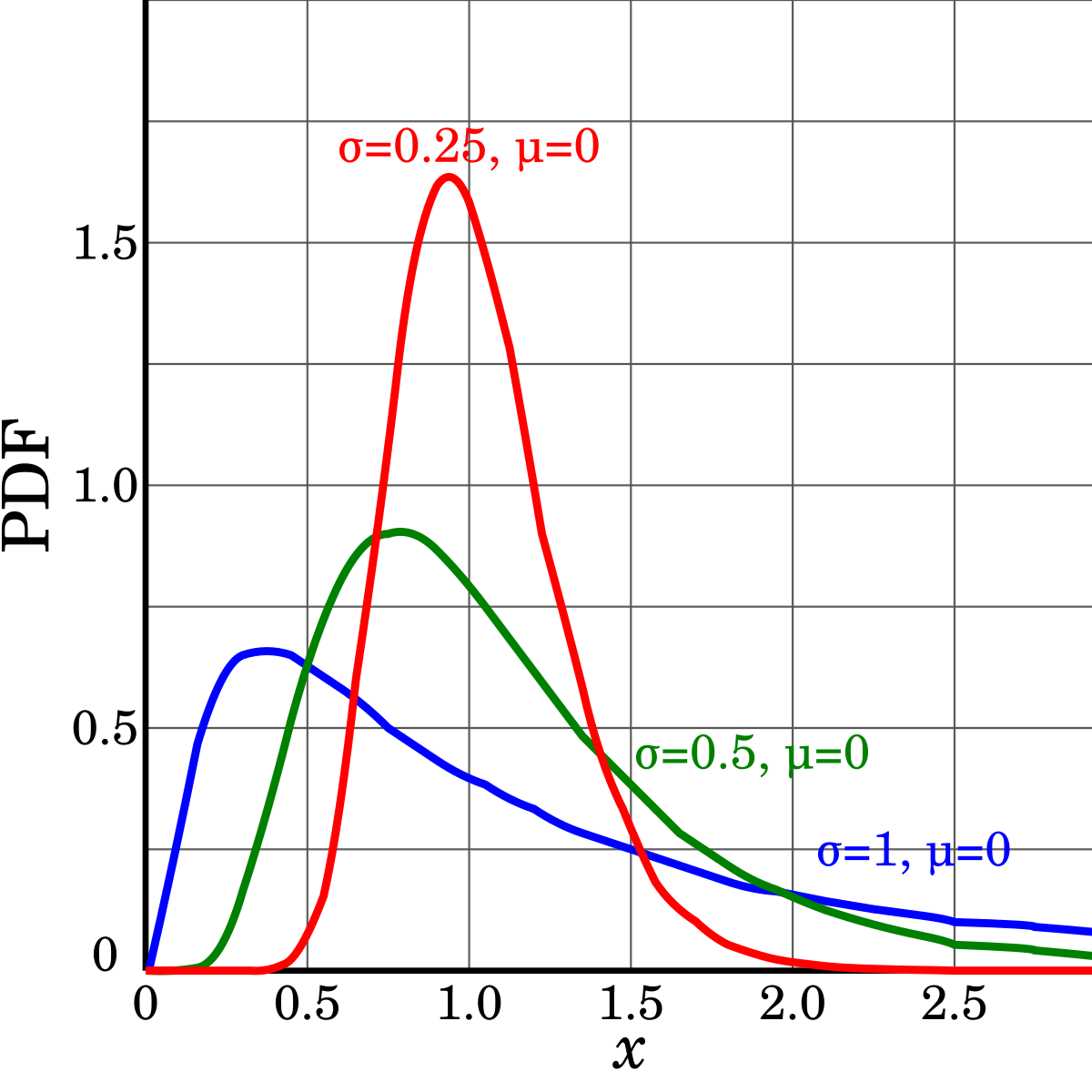
Log Normal Distribution Wikipedia

Inegalites De Sobolev Logarithmiques Et Hypercontractivite En Mecanique Statistique Et En E D P

A Classical Sequent Calculus With Dependent Types
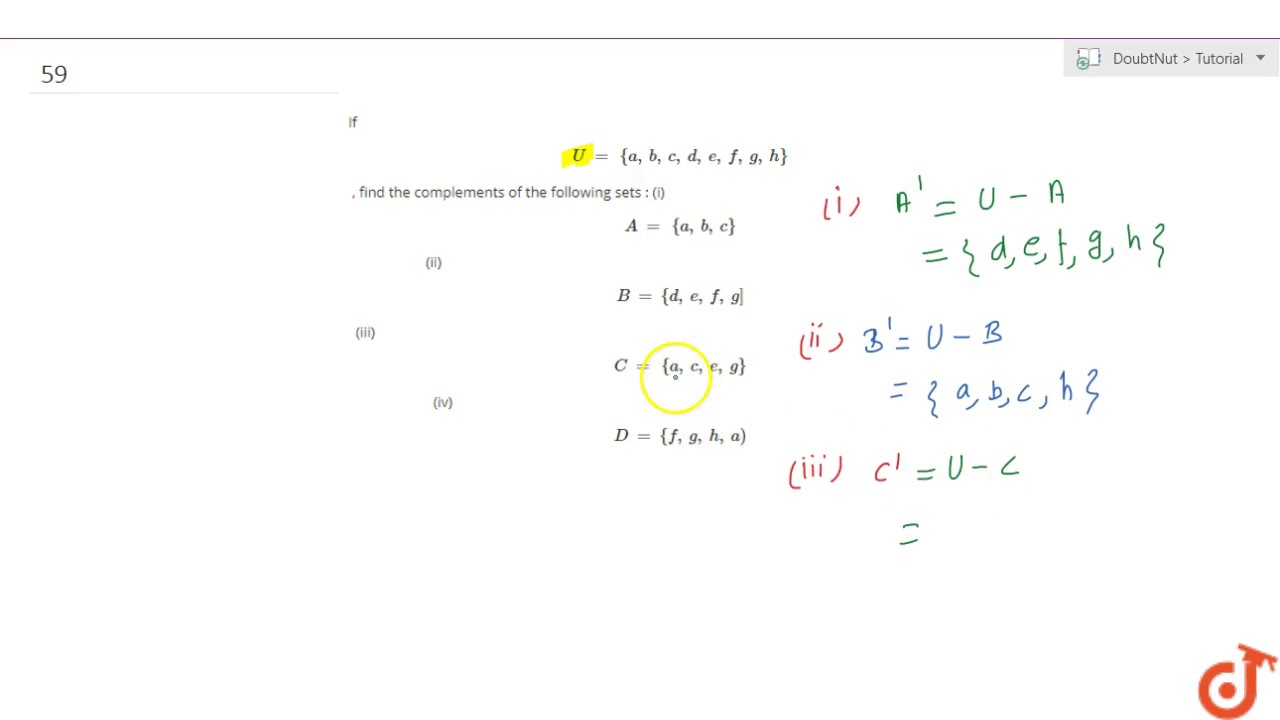
If U A B C D E F G H Find The Complements Of The Following Sets I A Youtube

Let A A B C D E F B C D E G And C B C F G Be Subsets Of T
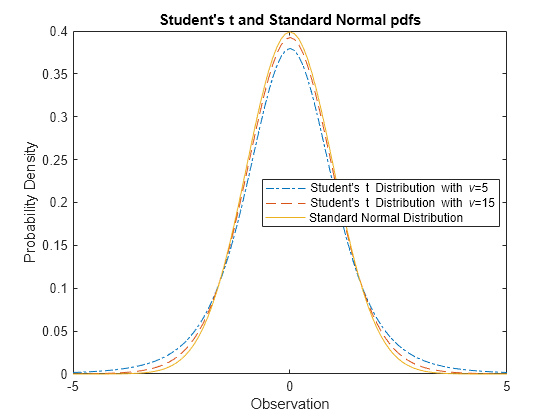
Normal Distribution Matlab Simulink

Gini Coefficient Wikipedia

Laplace Distribution Wikipedia
Osa Mathematical Model And Topology Evaluation Of Quantum Key Distribution Network

Bias Of An Estimator Wikipedia

Gamma Matrices Wikipedia

New Design Model Of Reinforced Concrete Beams In Bending Considering The Ductility Factor
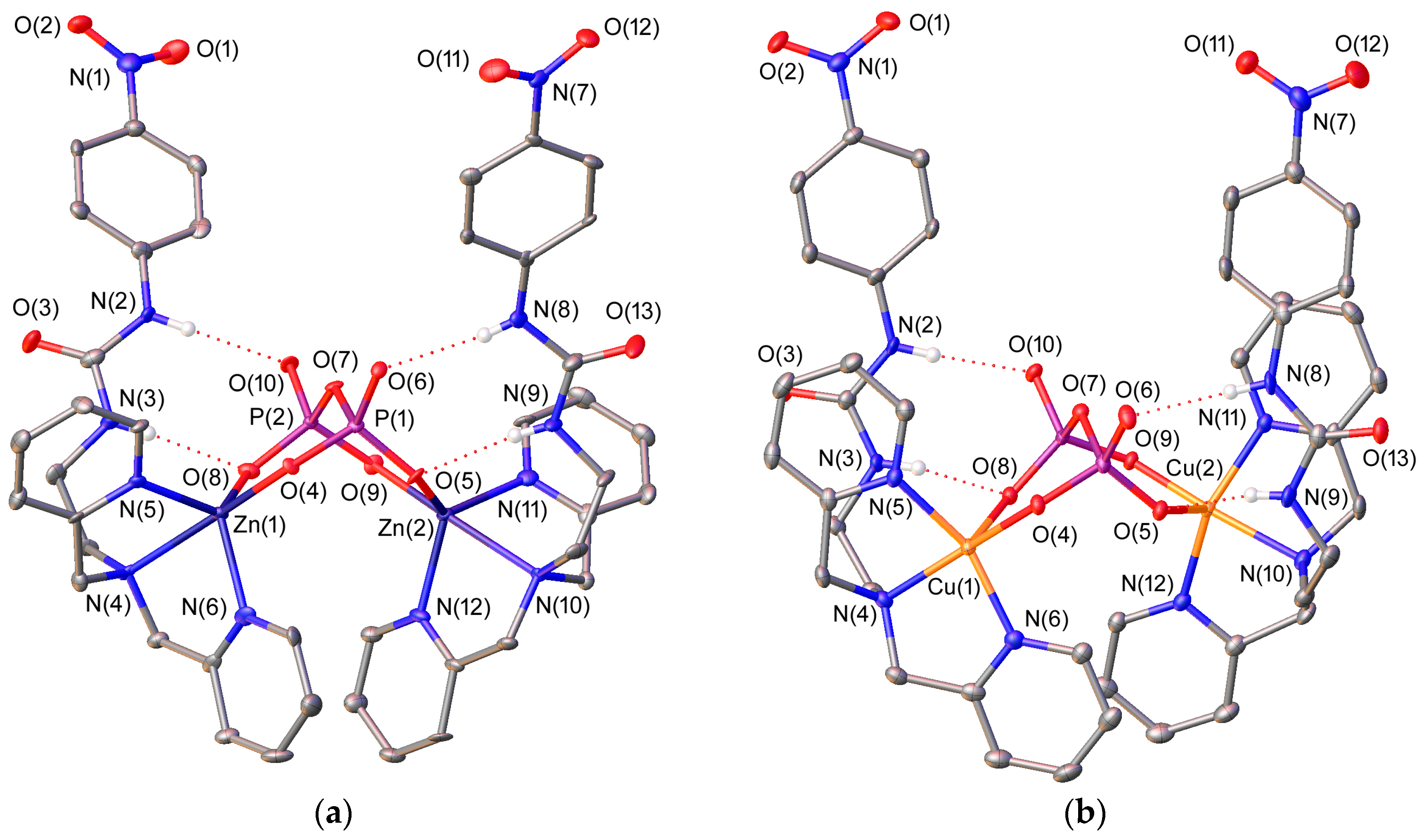
Molecules Free Full Text Recognition Of Amp Adp And Atp Through Cooperative Binding By Cu Ii And Zn Ii Complexes Containing Urea And Or Phenylboronic Acid Moieties Html

Correlation And Dependence Wikipedia

Pdf Effects Of Stress On The Mucus Microbial Interactions In The Gut
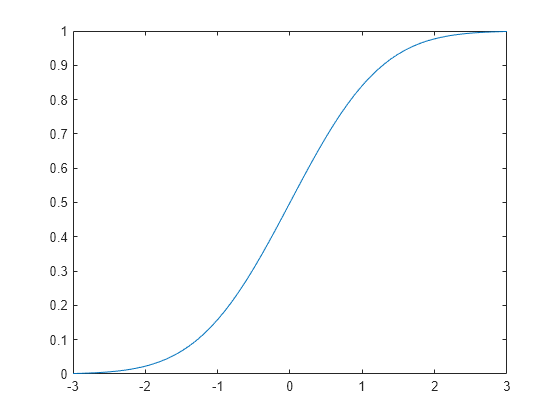
Normal Distribution Matlab Simulink

Lorentz Force Wikipedia

Gaussian Function Wikipedia
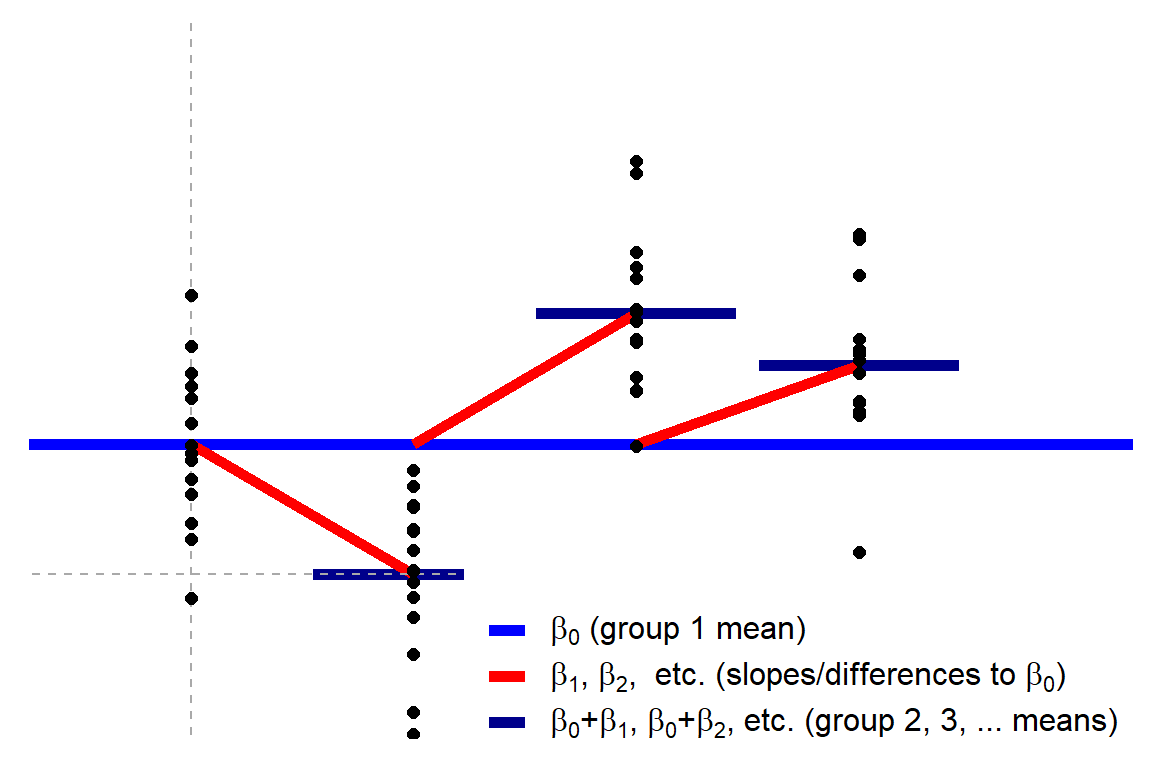
Common Statistical Tests Are Linear Models Or How To Teach Stats
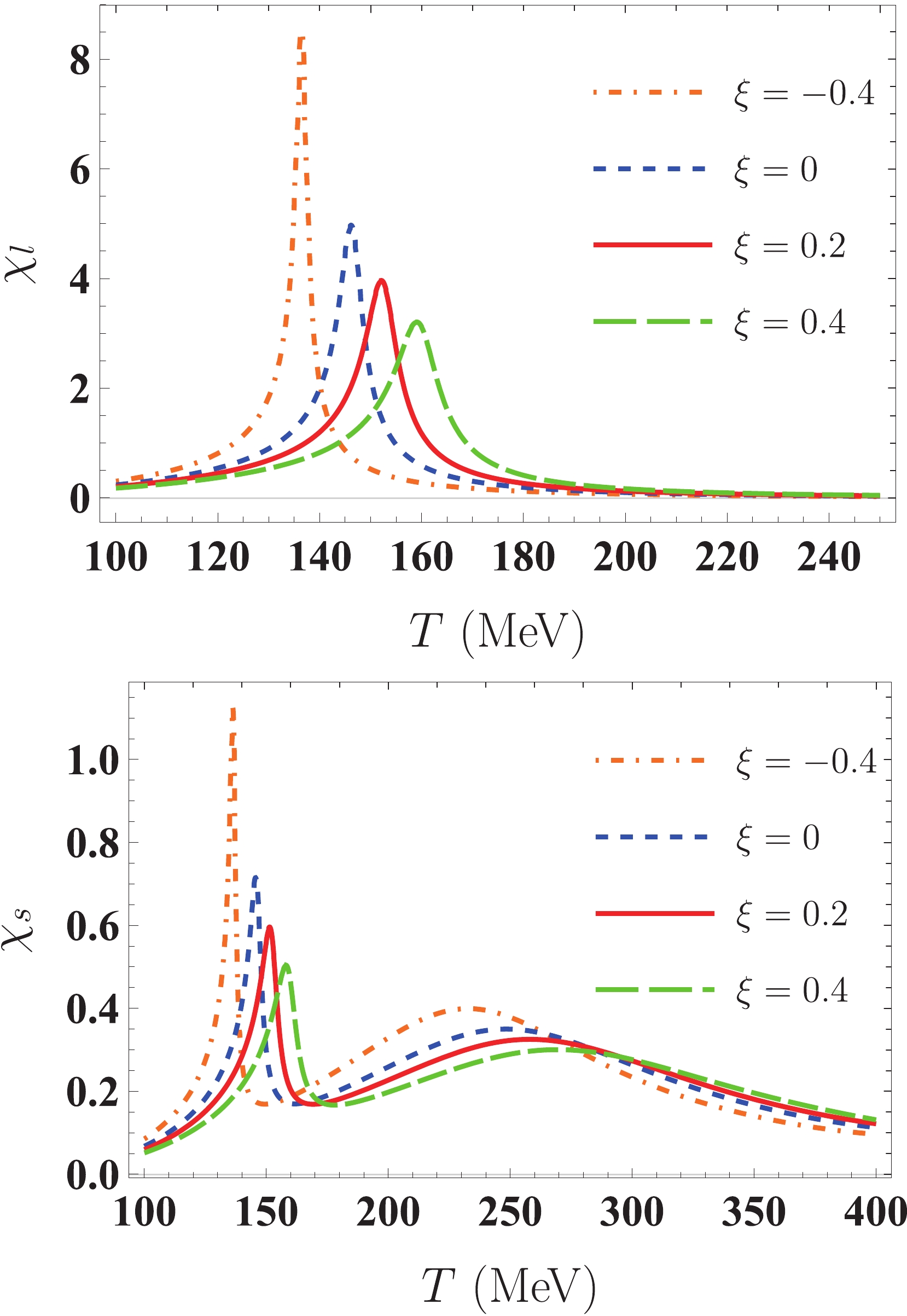
Effect Of Momentum Anisotropy On Quark Matter In The Quark Meson Model
Hgc 900 Single Mode Cellular Cdma Phone Test Report Hyundai Electronics Industries

Chorhhh

Bias Of An Estimator Wikipedia
Osa Mathematical Model And Topology Evaluation Of Quantum Key Distribution Network

Log Normal Distribution Wikipedia

Conformational Biosensors Reveal Allosteric Interactions Between Heterodimeric At1 Angiotensin And Prostaglandin F2a Receptors Journal Of Biological Chemistry
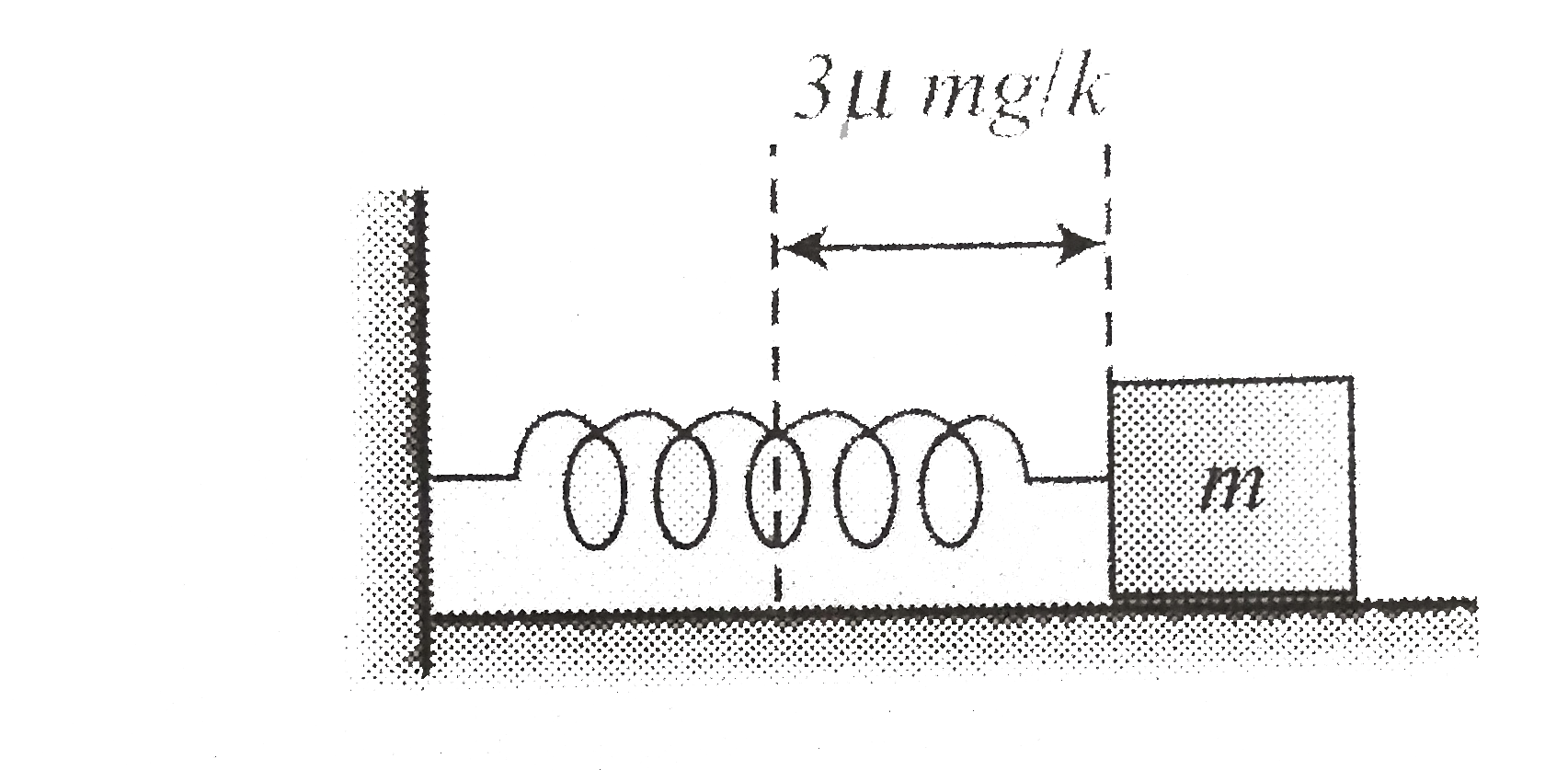
A Spring Block System Is Placed On A Rough Horizontal Surface Havi
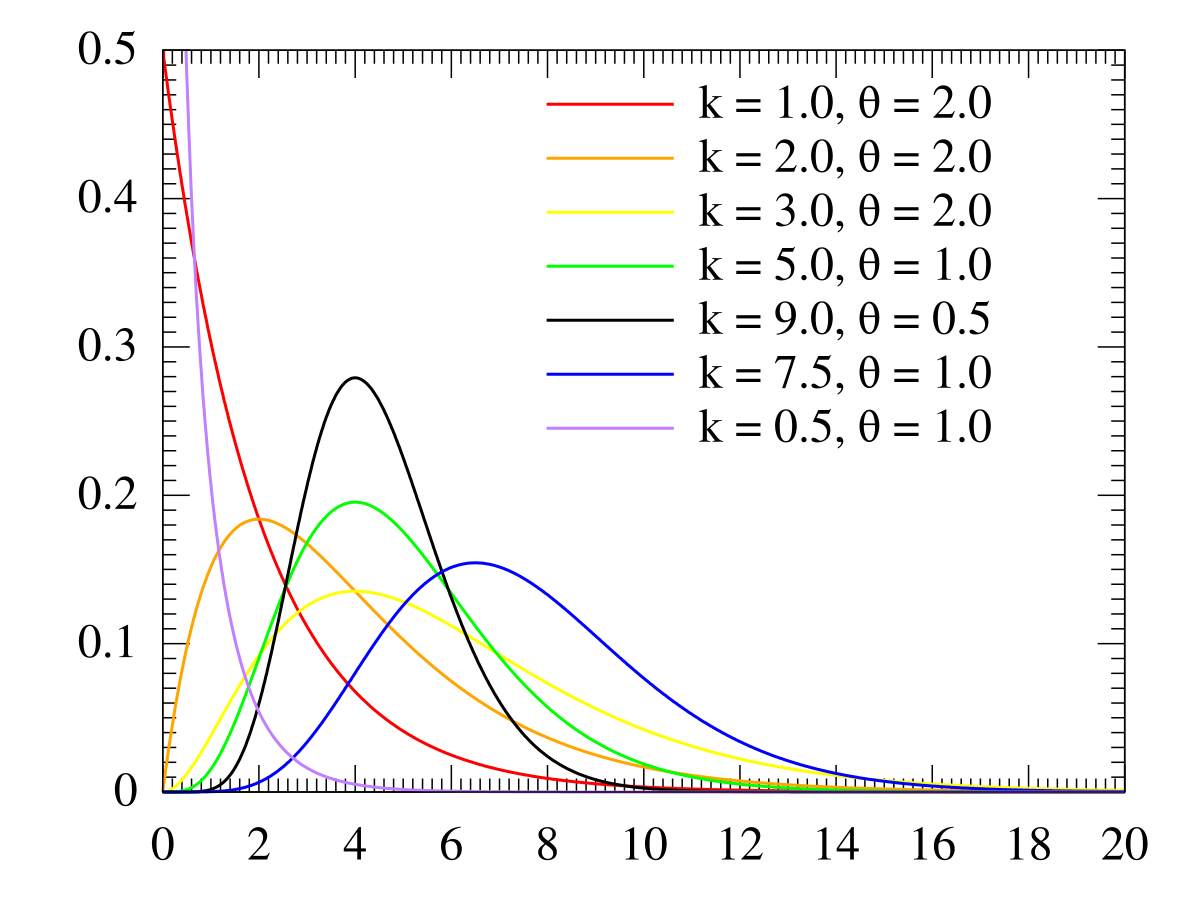
Gamma Distribution Wikipedia

Pdf Effects Of Shading On The Growth Development And Anthocyanin Content Of Echeveria Agavoides And E Marcus
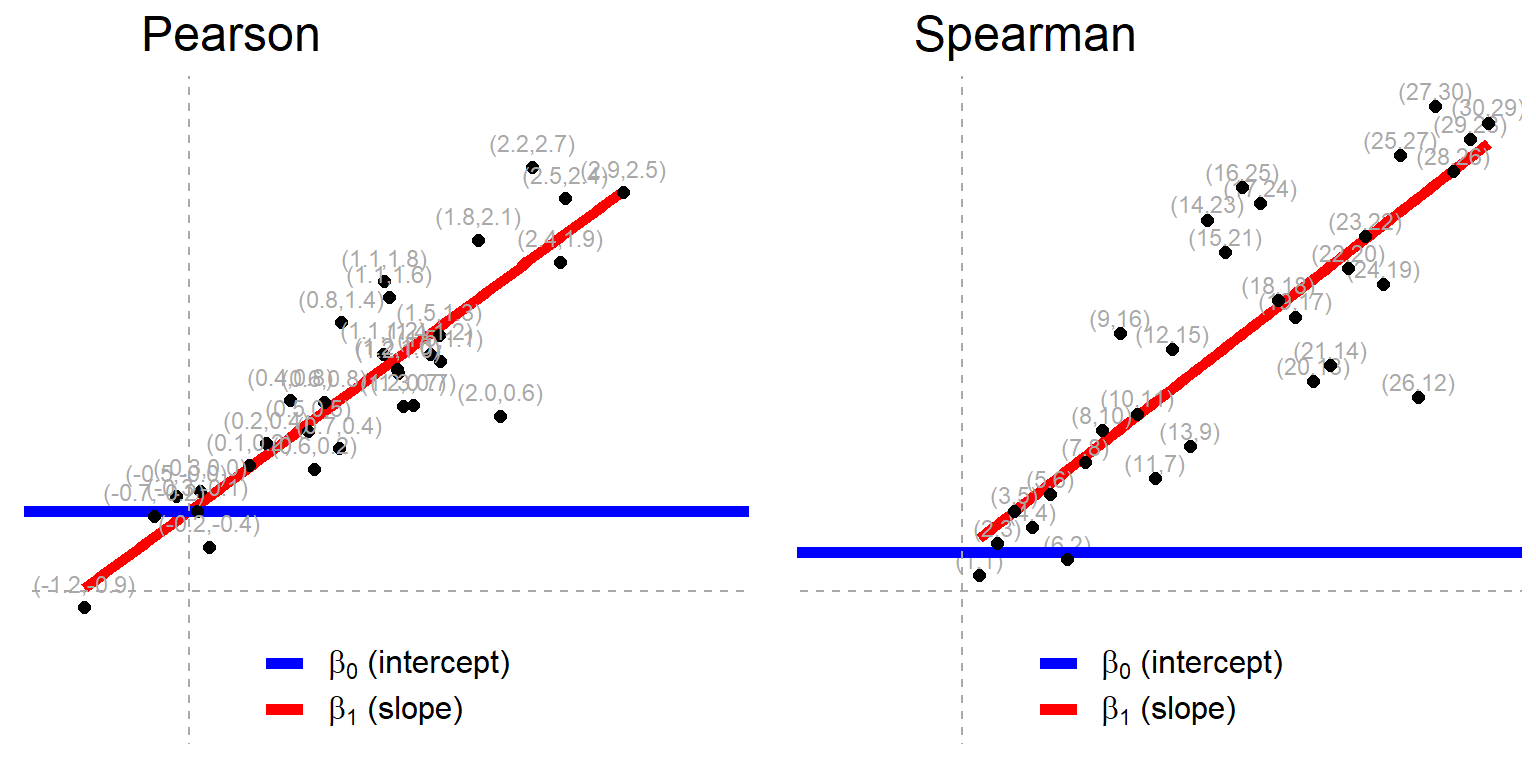
Common Statistical Tests Are Linear Models Or How To Teach Stats
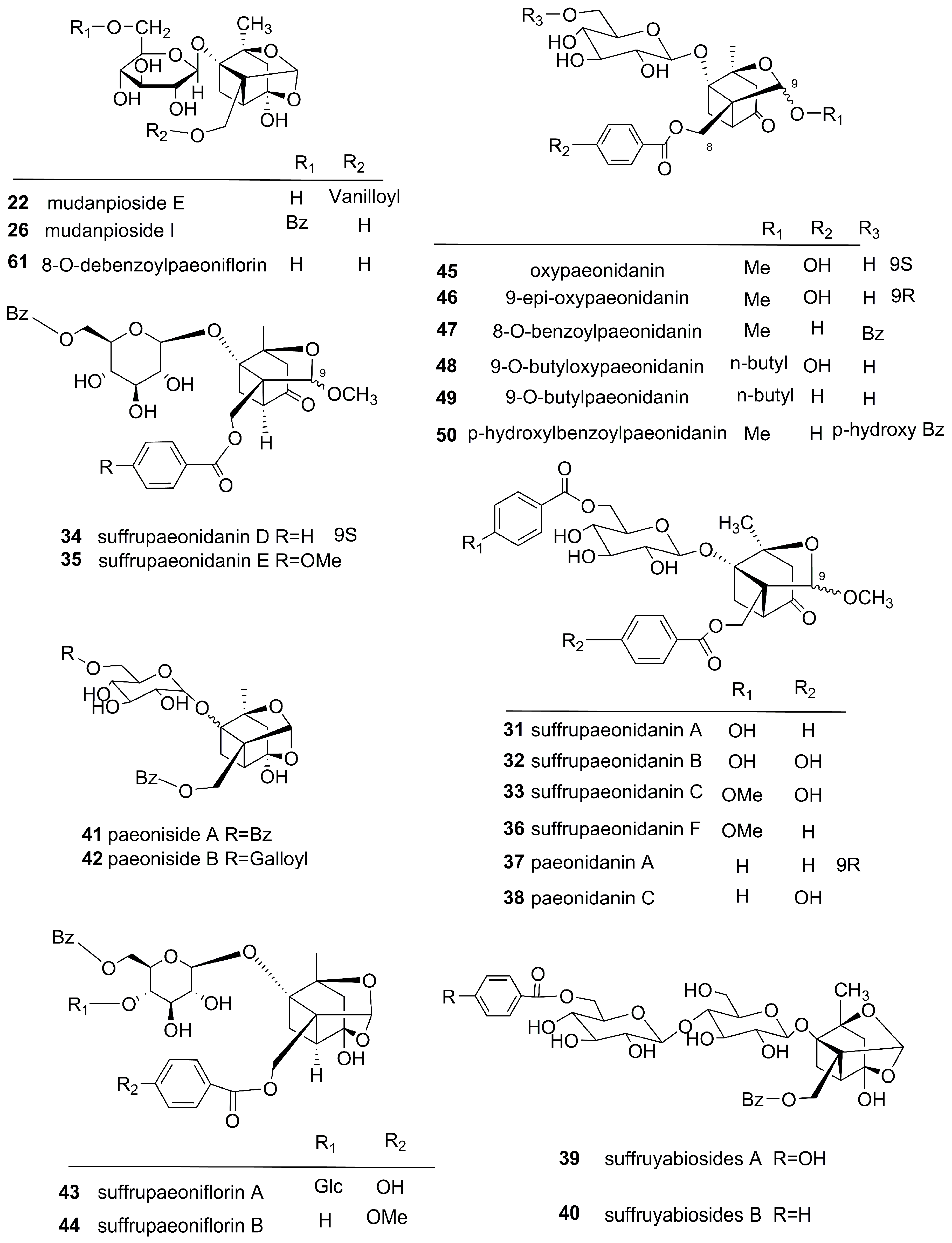
Molecules Free Full Text Origins Phytochemistry Pharmacology Analytical Methods And Safety Of Cortex Moutan Paeonia Suffruticosa Andrew A Systematic Review Html
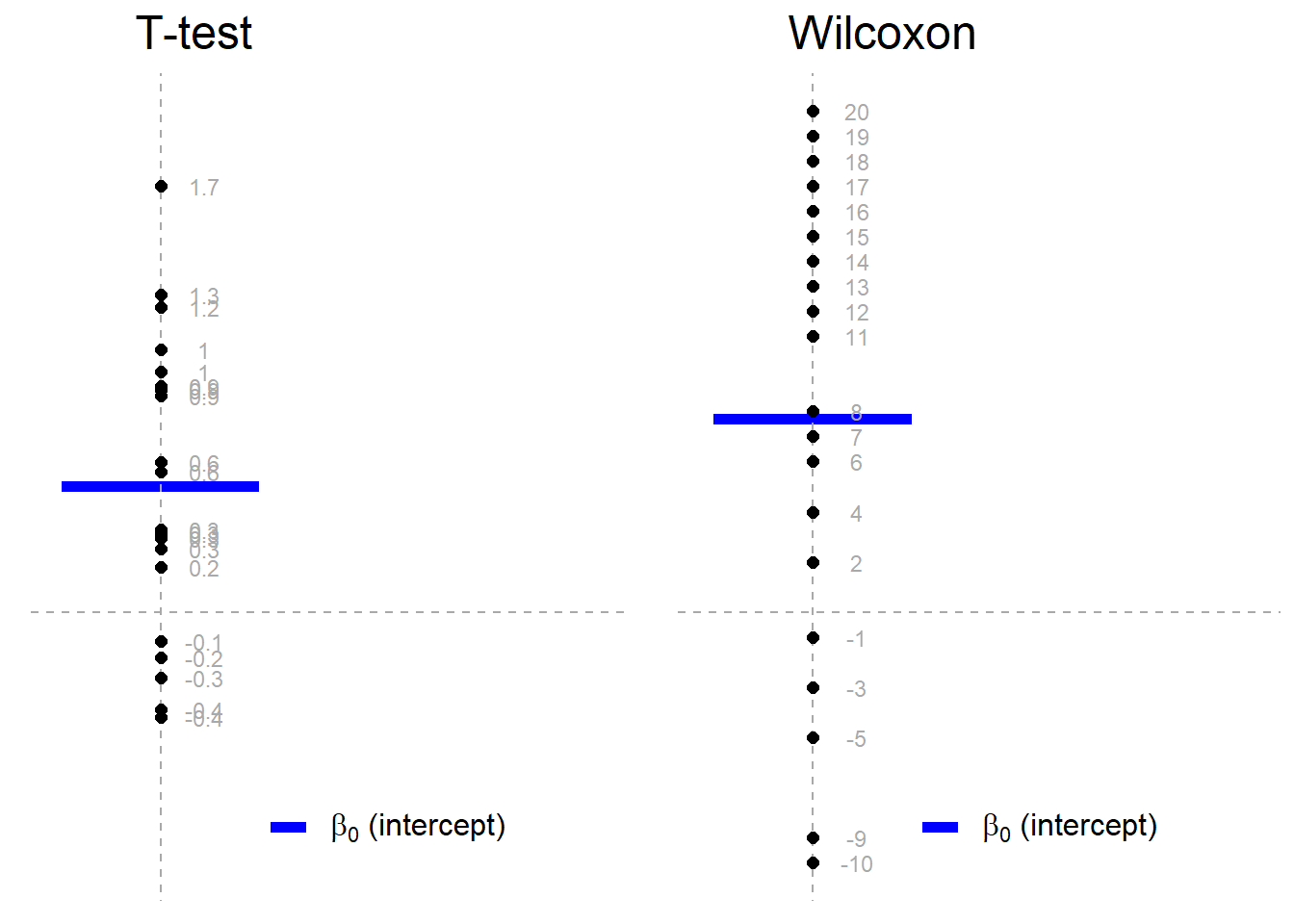
Common Statistical Tests Are Linear Models Or How To Teach Stats

Page 3 Ta Mu High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy
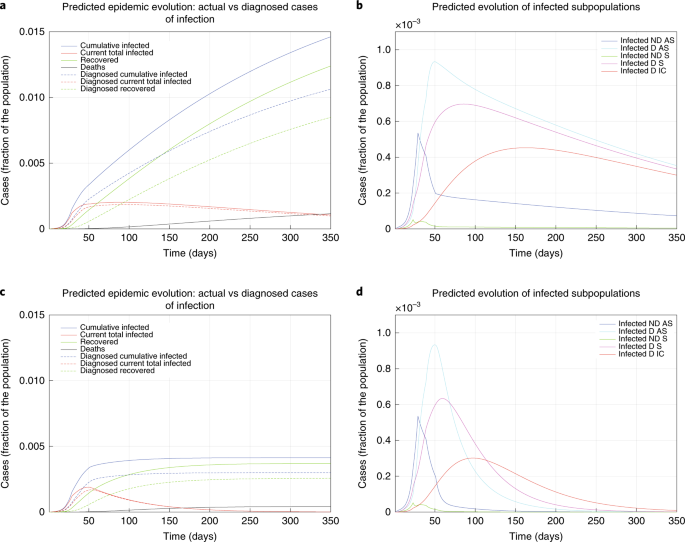
Modelling The Covid 19 Epidemic And Implementation Of Population Wide Interventions In Italy Nature Medicine
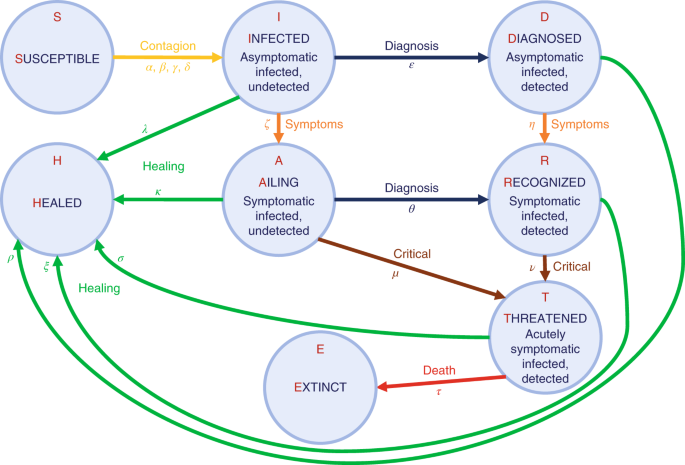
Modelling The Covid 19 Epidemic And Implementation Of Population Wide Interventions In Italy Nature Medicine

Insights Into The Composition Of Ancient Egyptian Red And Black Inks On Papyri Achieved By Synchrotron Based Microanalyses Pnas
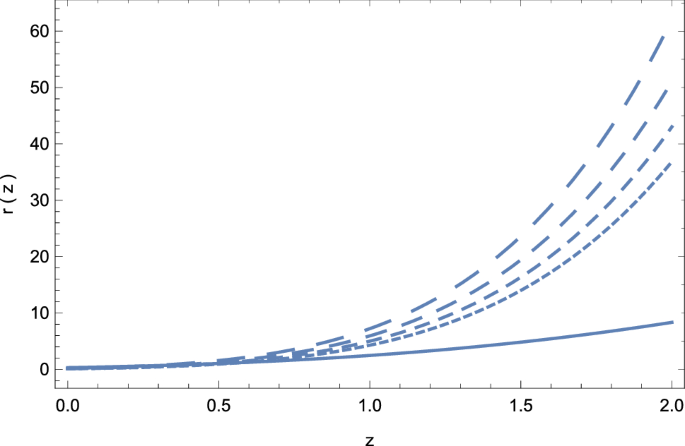
Weyl Type F Q T Gravity And Its Cosmological Implications Springerlink

A Classical Sequent Calculus With Dependent Types

Pdf Development Of A Global Evapotranspiration Algorithm Based On Modis And Global Meteorology Data

An Introduction To R
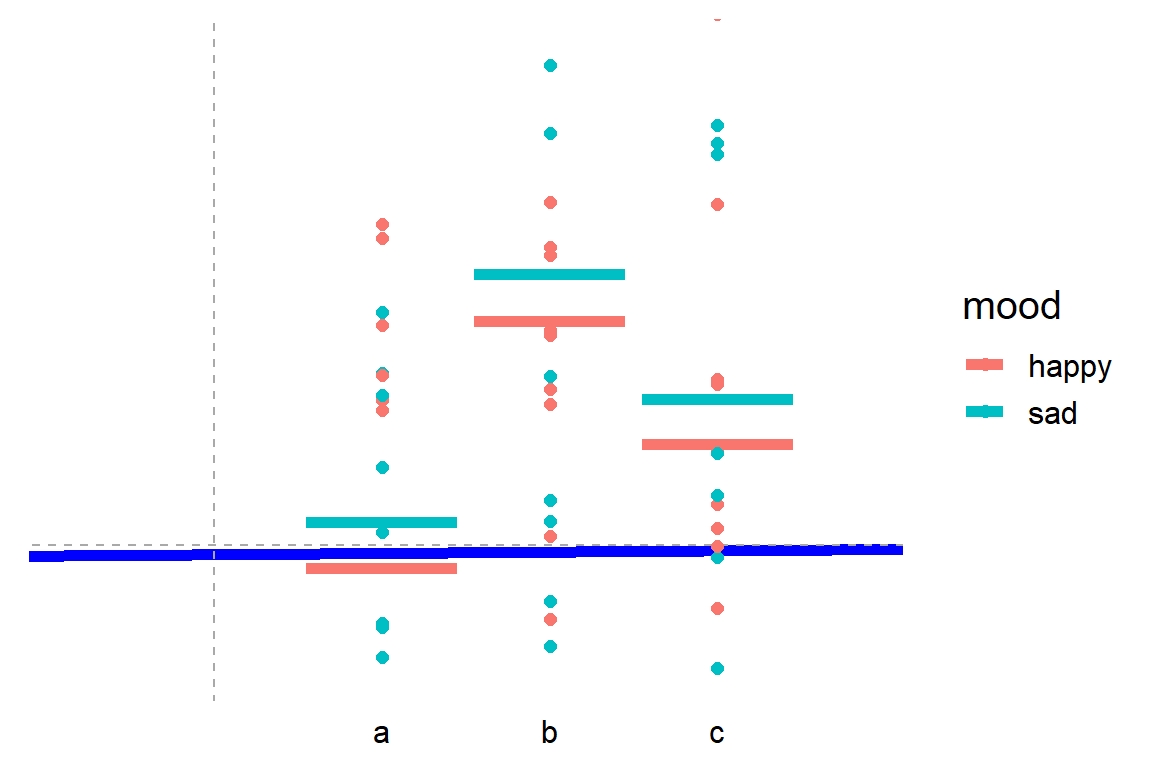
Common Statistical Tests Are Linear Models Or How To Teach Stats

An Introduction To R

Pdf Apple Scab Control And Activation Of Plant Defence Responses Using Potassium Phosphite And Chitosan

Ta Mu High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy
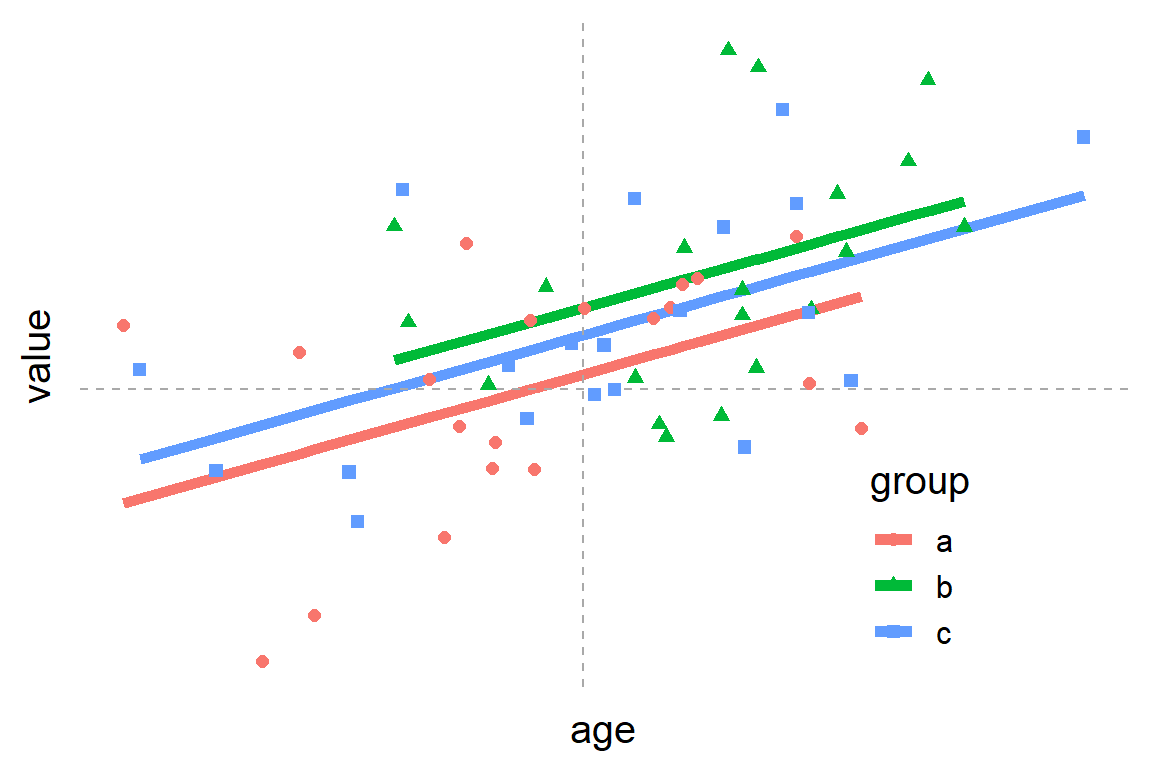
Common Statistical Tests Are Linear Models Or How To Teach Stats
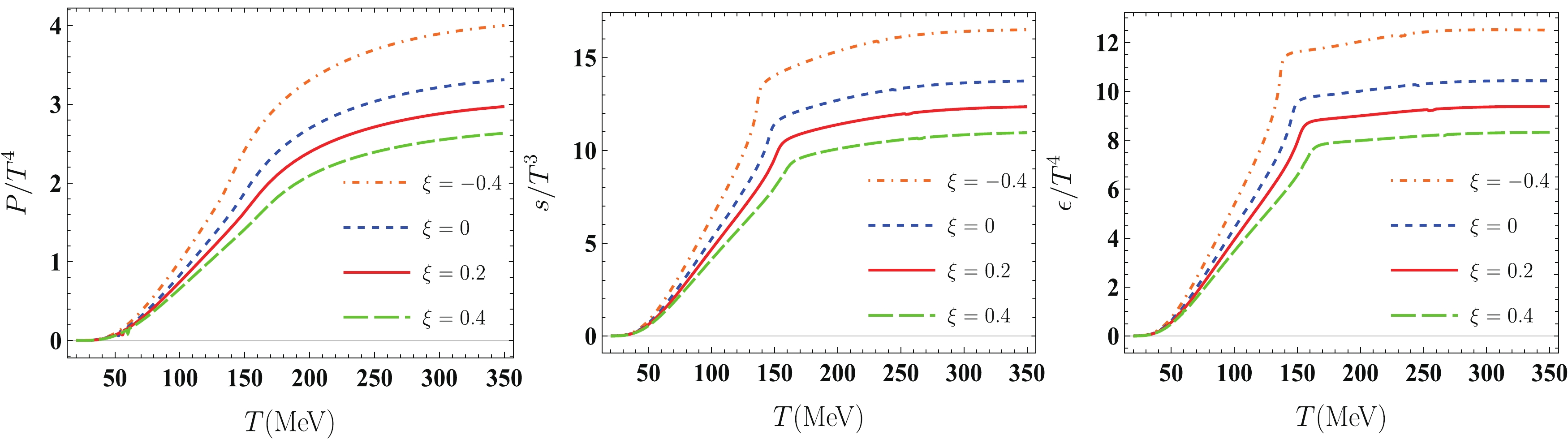
Effect Of Momentum Anisotropy On Quark Matter In The Quark Meson Model

From Migration To Inversion Velocity Analysis Geophysics
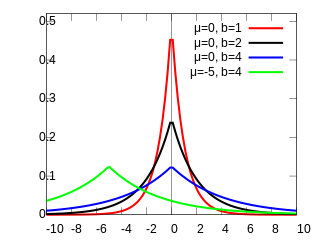
Laplace Distribution Wikipedia
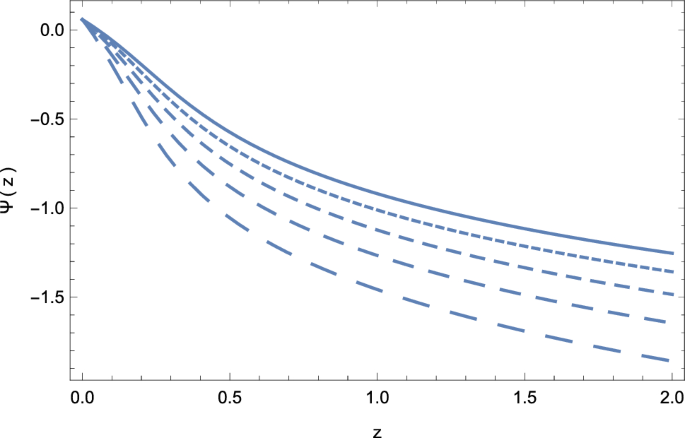
Weyl Type F Q T Gravity And Its Cosmological Implications Springerlink




